Choosing the right health insurance for your business can feel overwhelming. You might wonder: should you opt for small group health insurance or go with a large group plan?
The decision you make impacts not only your wallet but also the well-being of your employees. Understanding the key differences between small and large group health insurance plans can help you find the best fit for your team’s needs and budget.
Keep reading to uncover what sets these plans apart and how you can make a smarter, more informed choice for your business and your people.

Credit: www.associationhealthplans.com
Group Size Criteria
The size of a group plays a key role in health insurance plans. Group size determines eligibility, coverage options, and pricing. Understanding group size criteria helps businesses choose the right plan. Group size is mainly divided into small and large categories. These categories vary by state and insurer. Below are clear definitions and explanations.
Small Group Definition
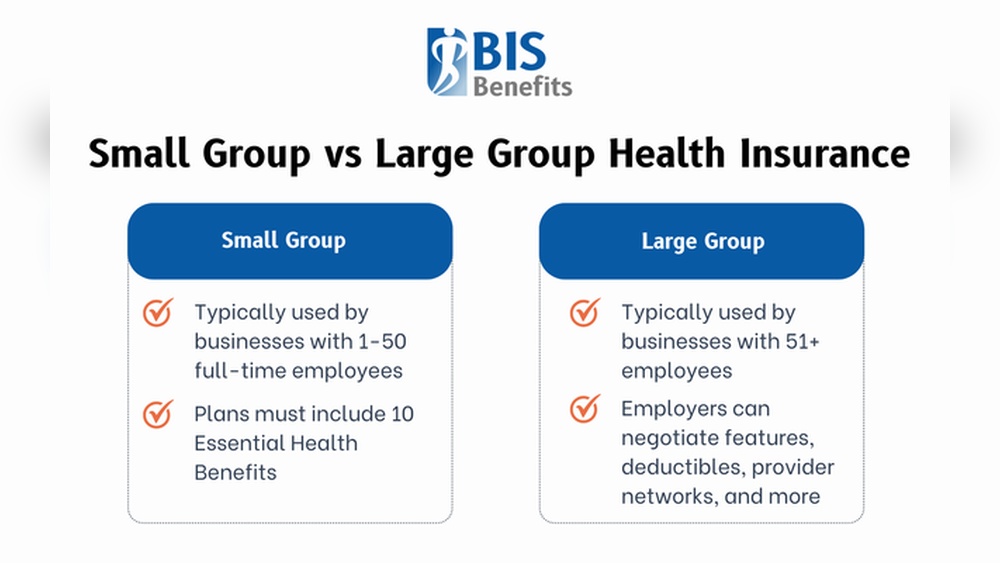
Small group health insurance usually covers fewer employees. The number often ranges from 1 to 50 or 100 employees. This limit depends on the state’s laws. Small groups benefit from simpler plans and tax credits. These plans often include essential health benefits and cover pre-existing conditions. Employers share premiums with employees, lowering individual costs.
Large Group Definition
Large group health insurance applies to bigger businesses. Typically, groups with more than 50 or 100 employees qualify as large. Large group plans offer more coverage options and flexibility. Employers have greater bargaining power to negotiate rates. These plans may include extensive medical, dental, and vision benefits. Large groups often experience more stable premiums due to risk spread.
State Variations
Each state sets its own rules for group size definitions. Some states define small groups as up to 50 employees. Others extend this to 100 employees or more. These variations affect plan availability and pricing. States also differ in regulations for eligibility and benefits. Employers must check local laws before choosing a group health plan. Understanding state rules ensures compliance and better coverage options.

Credit: www.plumhq.com
Eligibility Requirements
Eligibility requirements play a key role in deciding between small group and large group health insurance. These rules determine which employers and employees can join a plan. Understanding these criteria helps businesses choose the right coverage. The requirements focus mainly on employer size and employee participation. Both factors affect plan options and costs.
Employer Size Thresholds
Employer size is the main factor that separates small group from large group plans. Most states define a small group as having between 1 and 50 full-time employees. Some states extend this limit to 100 employees. Large group plans generally cover employers with more than 50 or 100 employees.
The exact number varies by state and insurer rules. Counting full-time equivalent employees is common. Part-time workers may be combined to count as full-time employees. This threshold affects plan pricing and benefits.
Employee Participation Rules
Employee participation rules require a minimum number of workers to join the plan. Insurers set these rules to keep risk balanced and premiums stable. Small group plans often require 70% to 75% of eligible employees to enroll.
Large group plans usually have lower participation demands or none at all. Some insurers require waiting periods before employees can join. Participation rules protect both the company and insurer from high costs. Employers must communicate clearly to meet these rules.
Plan Features
Plan features vary significantly between small group and large group health insurance. These differences affect coverage, costs, and services offered. Understanding these features helps businesses choose the right plan for their employees. Each type offers distinct options to meet diverse needs.
Coverage Options
Small group plans usually focus on essential health benefits. They often cover medical, pharmacy, dental, and vision care. Large group plans tend to offer broader coverage options. These may include specialized care and wellness programs. Coverage flexibility is greater in large group plans. Employers can customize plans to fit employee needs.
Benefit Tiers
Small group insurance commonly has fewer benefit tiers. These tiers range from basic to more comprehensive coverage. Large group plans typically provide multiple benefit tiers. Employees can select from bronze, silver, gold, or platinum levels. More options mean employees find plans matching their budget and health needs. This variety supports better employee satisfaction.
Additional Services
Additional services in small group plans are often limited. They may include basic wellness programs and telehealth. Large group plans usually offer extensive extra services. These include behavioral health support, wellness coaching, and health savings accounts. Large groups benefit from partnerships with health providers and clinics. These services promote better health and reduce costs.
Cost Factors
Cost plays a major role in choosing between small group and large group health insurance. Several factors influence the final price employers and employees pay. Understanding these cost factors helps in making a smart decision. Below, we explore key elements that affect insurance costs.
Premium Sharing
Employers and employees usually share the premium cost. In small groups, the employer often pays a larger portion. Large groups spread costs across many employees, lowering individual shares. This can make premiums more affordable for workers in large groups.
Risk Pooling Effects
Risk pooling means combining many people to balance health costs. Large groups have more members, creating a bigger risk pool. This lowers the chance of high costs from a few sick employees. Small groups have smaller pools, so costs can rise if one member needs expensive care.
Tax Credits
Small businesses may qualify for tax credits to reduce insurance costs. These credits help offset premiums and encourage coverage. Large groups generally do not receive the same tax benefits. Tax credits make small group plans more budget-friendly for employers.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance plays a crucial role in choosing between small group and large group health insurance. Each type must follow specific laws and rules. These regulations protect both employers and employees. They ensure fair access to health coverage and maintain plan quality. Understanding these requirements helps businesses avoid penalties and provide better benefits.
Aca Mandates
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) sets important rules for group health insurance. Both small and large groups must offer plans that meet ACA standards. These include coverage for pre-existing conditions and essential health benefits. Small group plans often have more flexibility in plan design than large group plans. Large group plans must also follow employer shared responsibility rules. This means they may face penalties if coverage is not offered to full-time employees.
State-specific Regulations
Each state has its own rules for group health insurance. These rules can affect plan types, benefits, and eligibility. Definitions of “small group” vary by state, usually based on the number of employees. Some states require additional benefits or consumer protections. Employers must check their state laws to ensure compliance. State rules often impact the cost and options available to businesses.
Alternatives For Small Businesses
Small businesses often face challenges in providing health insurance to their employees. Traditional group health plans can be costly and complex. Luckily, alternatives exist that offer flexibility and control. These options help small employers support their team’s health needs without large group plan constraints.
Ichra Explained
ICHRA stands for Individual Coverage Health Reimbursement Arrangement. It allows employers to give employees money to buy their own insurance. Employers set a budget, and employees choose plans that fit their needs. There are no limits on how much employers can contribute. Employers can also offer different amounts to different employee groups. This option provides flexibility and personal choice.
Qsehra Benefits
QSEHRA means Qualified Small Employer Health Reimbursement Arrangement. It is designed for businesses with fewer than 50 employees. Employers reimburse employees for medical expenses and health insurance premiums. The money is tax-free for both employer and employee. QSEHRA has contribution limits set by the government each year. It is easy to manage and helps small businesses offer health benefits affordably.
Plan Flexibility
Plan flexibility plays a key role in choosing health insurance for groups. It affects how well a plan meets the needs of employees and the company. Small and large groups often see different options and levels of flexibility. Understanding these differences helps businesses select the best coverage for their teams.
Ppo Vs Hmo Options
Small groups often have fewer plan choices. Many small group plans offer either PPO or HMO options. PPO plans allow more freedom to see any doctor. HMO plans require using a network of providers. Large groups usually get a wider range of plans. They might access more PPO and HMO options. This gives employees more control over their care. The choice between PPO and HMO can affect costs and coverage. Large groups tend to have better rates for PPO plans due to volume.
Employee Choice
Large groups often provide employees with multiple plan choices. This lets employees pick plans that fit their needs and budgets. Small groups may have limited options to choose from. Sometimes, small groups offer just one plan. Employee choice can improve satisfaction and reduce turnover. Large group plans may include more add-ons like dental or vision coverage. Small group plans might bundle these or offer them separately. Flexibility in plan design can attract and keep employees in larger companies.

Credit: www.healthinsurance.org
Cost Comparison
Comparing costs between small group and large group health insurance helps employers plan budgets. Insurance expenses vary based on the size of the group. Understanding this difference guides better financial decisions for businesses.
Per Employee Expenses
Small groups usually pay more per employee than large groups. Insurance companies see small groups as higher risk. This leads to higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs. Large groups spread risk over many employees, lowering per-person costs. Employers in large groups often share expenses with employees. This balance can reduce individual cost burdens significantly.
Impact Of Group Size
Group size directly affects insurance pricing. Larger groups benefit from economies of scale. Insurers offer discounts to attract bigger groups. Smaller groups face less negotiating power with insurers. They often receive fewer plan options at higher rates. A growing group can reduce costs over time. Employers should weigh these factors when choosing coverage.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Difference Between A Small Group And A Large Group?
A small group usually has fewer than 50 employees, while a large group has 50 or more. Small groups often get simpler health plans and different regulations. Large groups benefit from lower premiums due to risk spreading and more plan options.
What Is A Large Group Health Insurance?
Large group health insurance covers companies with 51 or more employees. It offers shared premiums, comprehensive benefits, and ACA compliance, reducing individual costs through pooled risk. Employers and employees typically share premiums, and plans often include medical, dental, and vision coverage, tailored to meet diverse workforce needs.
What Is Considered Small Group Insurance?
Small group insurance covers businesses with 1 to 50 employees, offering ACA-compliant health plans. It includes shared premiums, essential benefits, and varies by state regulations.
Is It Better To Have Ppo Or Hmo?
PPO plans offer more flexibility and no referrals for specialists. HMO plans usually cost less but require primary care and referrals. Choose PPO for freedom; choose HMO for lower costs and coordinated care. Your choice depends on budget and healthcare preferences.
Conclusion
Choosing between small group and large group health insurance depends on your business needs. Small groups often get personalized service and flexible plans. Large groups can benefit from lower premiums and broader coverage. Consider costs, employee size, and plan options carefully.
Each type offers unique advantages to fit different situations. Understanding these differences helps you make an informed choice. Keep your team’s health and budget in mind. The right insurance supports a healthier, happier workplace.