If you’re self-employed, finding the right health insurance can feel overwhelming. You don’t have the safety net of an employer’s plan, and costs can add up quickly.
But don’t worry—there are several options tailored just for you. Whether you want affordable coverage through the Health Insurance Marketplace or prefer private plans, understanding your choices can save you money and stress. You’ll discover the best health insurance options for self-employed individuals, how to qualify for subsidies, and tips to pick the plan that fits your unique needs.
Keep reading to take control of your health coverage and protect yourself and your family without breaking the bank.

Credit: www.healthplansinoregon.com
Aca Marketplace Plans
The ACA Marketplace Plans offer health insurance designed for self-employed individuals. These plans provide access to a variety of coverage options. They help protect your health and your finances. The Marketplace is a government-run platform where you can compare and buy plans. It suits people without employer-provided insurance. Plans vary in price and benefits to fit different budgets and needs.
Premium Tax Credits
Premium tax credits lower the cost of monthly insurance payments. These credits depend on your income and household size. They make health coverage more affordable for many self-employed workers. You apply for these credits when you sign up through the Marketplace. They reduce your premium upfront or as a tax refund later.
Essential Health Benefits
ACA plans cover essential health benefits required by law. These include doctor visits, hospital care, and prescription drugs. They also cover maternity care and mental health services. This coverage ensures you get the care you need. It protects you from high medical costs.
Coverage For Pre-existing Conditions
Marketplace plans must cover pre-existing conditions without extra charges. This means no one can be denied care due to past illnesses. Self-employed people with health issues get the same protections. This rule provides peace of mind and fair access to care.
Private Insurance
Private insurance offers a flexible way for self-employed individuals to secure health coverage. It allows you to choose plans that fit your specific needs and budget. This option can provide more control over your benefits compared to group plans.
Direct Purchase Options
You can buy private insurance directly from insurance companies. Many insurers offer individual plans tailored for self-employed people. These plans often come with various coverage levels and benefits. Purchasing directly means you deal straight with the insurer, without intermediaries.
Cost Considerations
Private insurance costs depend on age, location, and health status. Monthly premiums may be higher than group plans but vary widely. Deductibles and copayments also impact overall costs. Comparing plans helps find affordable options without sacrificing coverage.
Plan Variations
Private insurance plans differ in coverage, network size, and extra benefits. Some plans cover dental and vision, while others focus on basic health needs. You can select plans with different deductible amounts and out-of-pocket limits. This variety lets you pick what suits your health and budget best.
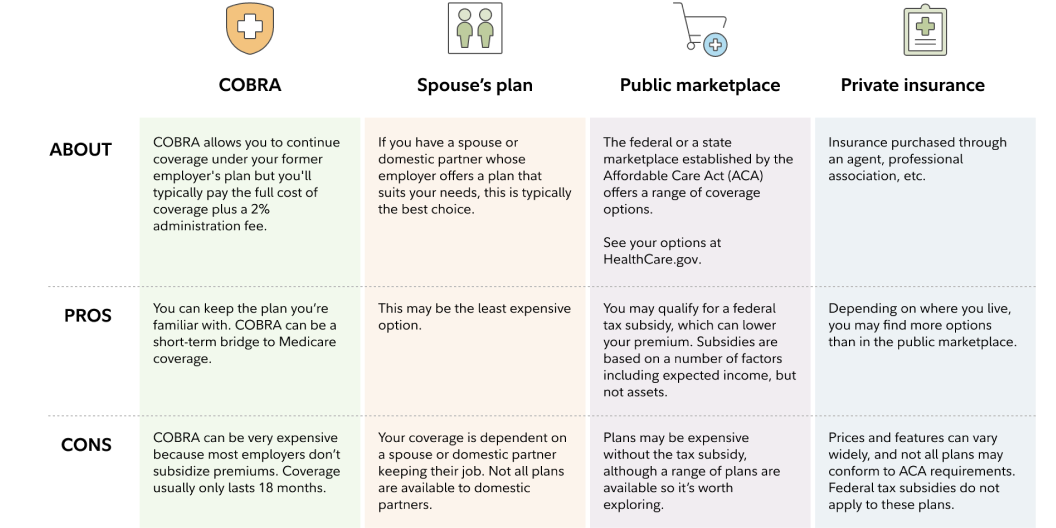
Cobra Coverage
COBRA coverage offers a way for self-employed individuals to keep their health insurance after leaving a job. It allows continuation of the previous employer’s group health plan. This option helps maintain health benefits without gaps in coverage.
Understanding COBRA’s rules can help you decide if it fits your needs. Costs and time limits matter most for self-employed workers. Knowing the pros and cons prepares you to make the right choice.
Eligibility And Duration
COBRA applies to employees and their families after job loss or reduced hours. You must have had health coverage from your employer. Coverage can last up to 18 months, sometimes longer with special circumstances. This gives time to find other insurance options.
Cost Factors
COBRA coverage costs more than regular employer plans. You pay the full premium plus a small administrative fee. This can be expensive for self-employed individuals. Budgeting for these costs is important before choosing COBRA.
Benefits And Drawbacks
COBRA keeps your current health plan and doctors. No new medical exams are needed to enroll. This is a big advantage if you have ongoing health needs. The downside is the high cost and limited coverage time. After COBRA ends, you need to find another plan quickly.
Spouse’s Employer Plan
The spouse’s employer plan can be a valuable health insurance option for self-employed individuals. This plan offers access to coverage through a partner’s workplace, often with stable benefits and predictable costs. It allows self-employed people to join an established group insurance plan without purchasing individual insurance.
Choosing this option can simplify the insurance process. The self-employed spouse gets covered under the employer’s plan, benefiting from comprehensive coverage and employer contributions. This approach often reduces monthly premiums and out-of-pocket costs.
Qualifying For Coverage
Typically, the self-employed spouse qualifies as a dependent on the employer’s health plan. Eligibility depends on the employer’s rules and the relationship status. Most plans allow spouses and sometimes domestic partners to enroll. Some plans require proof of marriage or partnership to add the self-employed spouse.
Enrollment usually happens during open enrollment periods or after a qualifying life event. Losing other health coverage or marriage can trigger special enrollment options. The self-employed spouse must meet these criteria to join the employer’s plan.
Cost Sharing
Cost sharing involves how much the self-employed spouse pays for premiums and medical expenses. Employers often cover a large portion of the premium, lowering the self-employed spouse’s monthly cost. The remaining premium is deducted from the employed spouse’s paycheck.
Other costs include copayments, deductibles, and coinsurance. These depend on the plan’s design and coverage level. Group plans tend to have lower deductibles and better cost-sharing than individual plans, saving money overall.
Coverage Details
Coverage through a spouse’s employer plan usually includes doctor visits, hospital stays, prescriptions, and preventive care. Many plans also cover mental health, maternity, and specialist services. The plan’s network of providers can be large, offering more choices for care.
The self-employed spouse should review the plan’s summary of benefits carefully. Some services might require prior approval or have limits. Understanding coverage details helps avoid unexpected costs and ensures the plan meets personal health needs.
Government Programs
Government programs offer key health insurance options for self-employed individuals. These programs provide coverage at reduced costs or no cost depending on eligibility. Understanding these programs helps you choose the best plan for your needs.
Medicaid Eligibility
Medicaid offers free or low-cost health coverage for low-income people. Eligibility depends on income, family size, and state rules. Self-employed workers with limited income may qualify for Medicaid. It covers doctor visits, hospital stays, prescriptions, and more.
Applying for Medicaid is simple through your state’s health department. Check your income against state limits to see if you qualify. Medicaid can reduce your health expenses significantly.
Medicare Options
Medicare is a federal health program for people 65 or older. Some younger self-employed people with disabilities can also get Medicare. It includes hospital insurance (Part A) and medical insurance (Part B).
Medicare Advantage (Part C) offers extra benefits through private insurers. Prescription drug coverage (Part D) is available too. Self-employed individuals can combine these plans for full coverage.
State-specific Programs
Some states run special health programs for self-employed residents. These programs may offer extra help or unique coverage options. Texas, California, and New York have programs designed for freelancers.
Check your state’s health department website for details. These programs can fill gaps left by federal options. They often provide affordable premiums and broader coverage.
Professional Association Plans
Professional association plans offer a unique health insurance option for the self-employed. These plans allow individuals to join groups related to their profession. By doing so, they gain access to insurance plans often reserved for larger groups. These plans can provide better coverage and lower costs. Self-employed workers benefit from the group buying power of these associations.
Group Rates
Professional associations negotiate group rates for their members. These rates are usually lower than individual plan costs. The savings come from pooling many members together. Insurers view these groups as less risky. This often leads to better pricing and more plan choices.
Membership Requirements
Each association sets its own membership rules. Some require proof of profession or licensing. Others ask for an annual fee. Membership may also need active work in the field. Checking these rules before joining is important. The goal is to ensure members fit the association’s profile.
Plan Features
Plans through professional associations often include comprehensive coverage. They may cover doctor visits, hospital stays, and prescriptions. Some plans offer dental and vision benefits. Members usually get access to wellness programs. These plans also provide peace of mind with reliable support services.
Family Floater Plans
Family floater plans provide health insurance coverage for the entire family under a single policy. These plans pool the sum insured and allow any family member to use it when needed. They offer simplicity by managing one policy instead of multiple individual plans.
Family floater plans suit self-employed individuals who want to protect their loved ones without buying separate policies. These plans cover spouses, children, and sometimes parents, depending on the insurer’s terms. This coverage helps reduce financial strain during medical emergencies.
Coverage Scope
Family floater plans cover hospitalization, surgeries, and daycare procedures. They include pre and post-hospitalization expenses too. Many plans offer coverage for maternity and newborn care. Some policies also cover critical illnesses and wellness benefits. The coverage amount is shared among all insured family members.
Cost Efficiency
These plans are cost-effective compared to buying individual policies. You pay one premium for the entire family’s health coverage. This lowers the overall premium amount while providing adequate protection. Insurers often give discounts for floater plans. Managing one policy also saves time and paperwork.
Ideal Candidates
Family floater plans suit self-employed people with small families. They work well for couples with children. These plans benefit families that want shared coverage without high costs. Those who prefer simple management of health policies find these plans useful. People seeking flexibility in using the sum insured also benefit.
Credit: www.fidelity.com
Tax Deductions For Self-employed
Tax deductions for self-employed individuals can reduce the cost of health insurance significantly. These deductions help lower taxable income by subtracting eligible expenses. Saving money on taxes makes health coverage more affordable for small business owners and freelancers.
Understanding which expenses qualify and how to file correctly is key. Smart planning allows maximizing these benefits to ease financial burdens related to health insurance.
Qualifying Expenses
Health insurance premiums paid for yourself, your spouse, and dependents qualify for deduction. This includes plans purchased through the marketplace or private insurers. You can also deduct premiums for dental and long-term care insurance. Only premiums for plans covering medical care count. Expenses must be paid out-of-pocket and not reimbursed.
Filing Tips
Report your health insurance deduction on Schedule 1 of Form 1040. Keep detailed records of premium payments and related documents. Deduct the amount on line 16 of Schedule 1. Self-employed individuals cannot deduct premiums if they or their spouse receive coverage from an employer. Use tax software or consult a tax professional to avoid errors.
Maximizing Benefits
Combine health insurance deductions with other business expenses to lower taxable income. Pay premiums early within the tax year to count them as deductible. Track all qualifying expenses carefully and separate personal from business costs. Consider a Health Savings Account (HSA) if paired with a high-deductible plan for extra tax savings. Staying organized helps claim the full deduction allowed.
Choosing The Right Plan
Choosing the right health insurance plan is crucial for self-employed individuals. The right plan offers protection without draining your finances. It provides peace of mind and access to quality care. Focus on what fits your personal and business needs. Consider coverage, costs, and benefits carefully. This guide helps break down key steps to select the best plan for you.
Assessing Coverage Needs
Start by reviewing your health requirements. Think about your current medical conditions. Include any regular prescriptions or treatments. Consider how often you visit doctors or specialists. Factor in your family’s health needs if they are covered. Decide if you want basic coverage or more comprehensive protection. Check if you need dental or vision plans. Understanding your needs prevents overpaying or underinsuring.
Budgeting For Premiums
Set a clear budget for monthly premiums. Balance affordable payments with sufficient coverage. Remember, cheaper plans may have higher out-of-pocket costs. Calculate deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance fees. Plan for unexpected medical expenses. Avoid plans that strain your finances or limit care. Review your income and expenses carefully. Prioritize plans that offer good value for your money.
Comparing Plan Benefits
Compare what each plan covers in detail. Look at hospital stays, doctor visits, and emergency care. Check if your preferred doctors or hospitals are included. Review prescription drug coverage and limits. Note any wellness programs or extra benefits. Consider the plan’s network size and flexibility. Read customer reviews for real user experiences. Choose plans that match your health needs and lifestyle.

Credit: www.healthforcalifornia.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Best Way For Self-employed People To Get Health Insurance?
Self-employed people should use the ACA Health Insurance Marketplace for flexible, affordable plans with possible tax credits. Consider spouse’s employer plan or government programs too. Choose plans covering essential health benefits for comprehensive protection.
What Type Of Insurance Should A Self-employed Person Have?
Self-employed individuals should have health insurance, business liability, professional liability, and property insurance. Health plans from the ACA Marketplace offer flexible, affordable coverage with tax benefits. Family floater health insurance is ideal for covering the entire household under one policy.
Which Insurance Is Best For Self-employed?
The best insurance for self-employed individuals is an ACA Marketplace plan. It offers affordable, comprehensive coverage with tax credits. Family floater health insurance also suits those needing coverage for dependents under one sum insured. Consider business liability insurance to protect your enterprise.
Is Health Insurance 100% Deductible For Self-employed?
Self-employed individuals can deduct 100% of health insurance premiums from their taxable income. The deduction applies if they report a net profit. This deduction reduces adjusted gross income, lowering overall taxes. It excludes premiums paid while eligible for other employer plans or government programs.
Conclusion
Choosing the right health insurance is important for self-employed workers. Plans vary in cost and coverage, so explore your options carefully. Consider your health needs and budget before deciding. Government marketplaces often offer affordable choices. Some plans cover families under one policy.
Don’t forget to check for possible tax deductions. Staying insured protects your health and finances. Taking time now can save stress later. Health coverage helps you focus on growing your business with peace of mind.

